

“Enneagram” literally means nine-sided diagram. Each point on the Enneagram represents one of the nine personality types in this typology system.
Basic History
The Enneagram has been used for centuries for personal development and was officially brought to the public in 1915 by philosopher, George Gurdjieff. In the 1960s Oscar Ichazo placed nine personality types on the Enneagram and Berkeley psychologists developed it further from there. It is now used by coaches, leaders, businesses, and individuals around the world to promote personal growth and better decision-making.
How It Works
The nine points on the diagram are equally spaced apart and represent nine basic personality types. Although each person emerges from childhood preferring one basic personality over the rest, according to this theory, every person has all nine types inside them. The inner lines of the Enneagram represent relationships, patterns, and similarities between the nine types.
In this system, no type is better than any other type and the numbers are an arbitrary way of distinguishing one from the other. During one’s lifetime it is not possible to “hop” or “change” types but it is possible to fluctuate expression from healthy, average, to unhealthy. Each type has a unique set of challenges, strengths, core values, and core fears. The nine types are labeled as follows:
- Type One “The Reformer”
- Type Two “The Helper”
- Type Three “The Achiever”
- Type Four “The Individualist”
- Type Five “The Investigator”
- Type Six “The Loyalist”
- Type Seven “The Enthusiast”
- Type Eight “The Challenger”
- Type Nine “The Peacemaker”
Three Centers of Intelligence
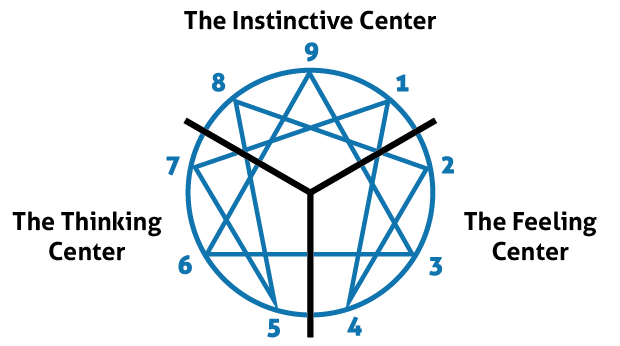
The Enneagram is organized into three centers of intelligence with three types falling into each category. Each type has unique strengths and liabilities associated with their triad.
- The Instinctive Center with Eight, Nine, and One are grounded and alive in their body. They often face the emotion of anger/rage.
- The Thinking Center with Five, Six, and Seven have a quiet and trusting mind. They often face the emotion of fear.
- The Feeling Center Two, Three, and Four have a receptive and authentic heart. They often face the emotion of shame.
Each type has a unique way of coping with the dominant emotion in their center.
In the Instinctive Center, Eights let anger build inside them and often express it physically, Nines deny anger and are most out-of-touch with their instincts, Ones try to control anger so that they can control their outcomes.
In the Thinking Center, Fives cope with fear by withdrawing from the world, Sixes exhibit the most fear and struggle with anxiety, Sevens fear the darkness of their inner world and distract themselves from it.
In the Feeling Center, Twos try to get ahead of shame by becoming likable, Threes deny their shame and are most out-of-touch with their feelings, Fours control their shame by expressing their individuality.
Adjacent Wings
Since no one person is a pure expression of any one type, wings play a major role in expressing type diversity within the Enneagram. Wings can be one of two types adjacent to your type (so an Enneagram Three can only be an Enneagram 3w2 or an Enneagram 3w4). The average person has access to both wings but leans more dominantly into one or the other.
Levels of Development
Within each of the nine personality types there is a continuum of growth ranging from healthy to average to unhealthy. On this continuum is a set of attitudes and behaviors unique to each person. Therapists and counselors often use the levels to pinpoint where a client is within their personal growth.
Within the Healthy, Average, and Unhealthy sections there are three additional levels:
- Healthy Level 1: The level of liberation
- Healthy Level 2: The level of psychology capacity
- Healthy Level 3: The level of social value
- Average Level 4: The level of imbalance/social role
- Average Level 5: The level of interpersonal control
- Average Level 6: The level of overcompensation
- Unhealthy Level 7: The level of violation
- Unhealthy Level 8: The level of obsession and compulsion
- Unhealthy Level 9: The level of pathological destructiveness
Movement up the levels is a measure of capacity to be present. Movement down the levels is a measure of proximity to the ego. Healthy expression of each type is marked by awareness in body, heart, and mind while unhealthy expression of each type is marked by defensiveness and compulsiveness.
Fun Fact: Wherever you are in terms of these levels, when you lean into the wing adjacent to your type, you will lean into the behaviors of that type at that same level. So if you are an Enneagram 9w8 at an “Average Level 4” you will show behaviors of a Nine at that level and an Eight at that level.
Directions of Growth and Stress
The inner lines of the Enneagram connect the type in a sequence of growth (integration) and stress (disintegration). Different situations will evoke either a growth response or stress response and in that reaction one type will adapt traits of another type.
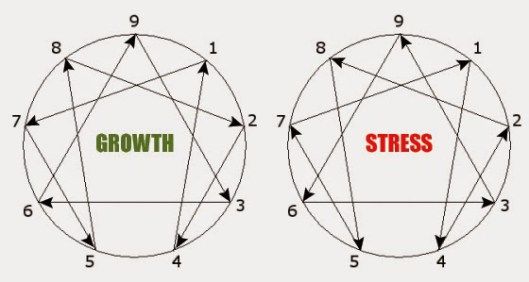
The Direction of Disintegration goes as follows: 1-4-2-8-5-7-1 and for the equilateral triangle, 9-6-3-9.
The Direction of Integration goes as follows: 1-7-5-8-2-4-1 and for the equilateral triangle, 9-3-6-9.
In times of stress, for example, an Enneagram Five will act out and behave like an average-unhealthy seven and might become avoidant of pain, spontaneous in action, and sensation-seeking. In times of growth, however, an Enneagram Five will integrate to a type eight and will be confident in their abilities, strong leaders, and bold adversaries.
Three Stances
Similar to the Centers of Intelligence, the three stances of the Enneagram paint an important picture of each unique type. These stances describe how each type handles conflict and moves through the world.
The Aggressive Stance includes Three, Seven, and Eight. In times of conflict they move toward what they want. They are all about controlling their destiny, moving quickly, and orienting others to their ideas.
The Dependent Stance includes One, Two, and Six. In times of conflict they refer to other people. They are concerned with the collective good, making connections, and determining what needs to be done.
The Withdrawn Stance includes Four, Five, and Nine. In times of conflict they move away from the world. These types try to stay independent and rely on their own strength, they may feel their presence won’t make a difference, and they might settle on a solution resentfully.
Three Instincts
The three instincts of the Enneagram, also be called the subtypes, are basic instincts present in every human being. Although all three exist in the body, one will be a driving force.
Self-Preservation (sp) types are concerned with safety, comfort, and guarding the physical self. They are worried about having enough resources to survive and fulfill their needs. These types tend to be more grounded and realistic than other types. They are protective, reliable, and stable.
Sexual/Intimate (sx) types are concerned with one-on-one connection and depth. They are aware of chemistry between themselves and other people and look for healthy relational stimulation. These types enjoy being caught up in the moment and often look at life through a romantic lens.
Social (soc) types are concerned with their social standing and whether or not they are accepted by the tribe. They are highly aware of others and will adapt themselves to the needs of the group. These types are engaging, warm, and more socially aware than the other two instinctual types.
Explore the Types
**Individual Type Pages Coming Soon!**
In the meantime, follow us on Instagram for more Enneagram content.